2 called methylene halide eg. 3 halides 2 halides 1 halides Alkyl halides also undergo ER in the presence of base as Nu Loss of HX and formation of bond H R OR CH2 CH2 Cl ROH CH3CHCH2 Cl CH3 ii In general 3 halides tend to react by elimination.

Solved Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Begin Array L Text A Chlorobenzene Text B 1 Text Bromo 4 Chlorohexane Text C 1 2 Text Difluoro 3 Iodocyclohexane
Define functional group and name the group present in each of the following structures.

. They can also be manufactured from any organic precursors such as alkanes alkenes or alcohols and carboxylic acids. They form a homologous series represented by C n H. CCl 4 is carbon tet More Classification of Alkyl Halides Methyl halides.
Implied double bond on the carbon fluorine is attached to CH₃CL₃ chloroform Alkyl Halide Bromocyclohexane Alkyl Halide. More than one of these is correct. This is an unsaturated structure due to the presence of double bonds in the aromatic ring.
An aryl halide is a molecule having a halogen atom attached to an sp2 hybridized carbon in an aromatic ring directly. Alkyl halides are the monohalogen derivatives of alkanes. Alkyl and Aryl Halides of Class 12 Aryl halides are compounds containing halogen attached directly to an aromatic ring.
Alkyl halide structures can be classified as primary secondary and tertiary. Generally alkyl halides contain hydrogen atoms attached to the sp. In alkyl halides the halogen atom is bonded to an alkyl group R.
The haloalkanes also known as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides are a group of chemical compounds consisting of alkanes such as methane or ethane with one or more halogens linked such as chlorine or fluorine making them a type of organic halide. Yeah we have to name this uh organic compound and for naming first important point to remember is that count the number of carbon atoms presenting the longest gene. The carbon-halogen bond is stronger than that of alkyl halides due to the presence of ring electrons.
CH 2 Cl 2 is methylene chloride CHX 3 is a haloformeg. How can you test the purity of chloroform. Draw the structures of all the eight structural isomers that have the.
Methyl halide Isobutyl halide. Draw structures for these alkyl and aryl halides. The halogen pulls electrons away from the carbon making it more reactive.
Organohalogen compounds are roughly classified into two groups. With their assist you can make not merely a novel nail design but a magnetic picture the principle concentration of that can be your sparkling nails. CH3Br CH32CHBr CH33 CBr.
In addition there are halogenated alkenes and alkynes. Aryl halides are always ringed structures. Organic halogen compounds used in industry as solvents are chlorides rather than bromides and iodides.
The halogen atom is attached to a sp 2 hybridized carbon atom in aryl halides. Alkyl halides are organic compounds having halogen atoms covalently attached to aliphatic carbon atoms or carbon atoms in a straight hydrocarbon orientation. 122 Alkyl Halides Aryl Halides and Aromatic Compounds Common system.
1234 Carbon atoms representing longest chain. 101 Naming alkyl halides- Read 102 Structure of alkyl halides Table 101 Halomethane H3C-F H3C-Cl H3C-Br H3C-I Bond length pm 139 178 193 214 Bond strength KJmol 452 351 293 234 Dipole Moment 185 187 181 162 RCC _ Na CX H R H THF RCCC R H NaX The significant dipole moment of alkyl halides make then good electrophiles for substitution reactions. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
Draw structures for the following molecules. Which of the following is most reactive towards SN2 reaction. 1 halides by substitution and 2 halides by either or both of the reactions.
The alkyl can easily leave on its own. An aryl halide is not just. Alkyl halides have a linear or branched structure most of the times.
ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES ALKYL AND ARYL HALIDES Very short answer type questions Q1. Cl F Br iso-butyl chloride hexyl f luoride t- buyromide 3. The name of the alkyl group and halide are written as two separate words.
Draw the structure of an alkyl halide that could be used in an E2 reaction to give the following alkene as the only alkene product. The chemical reactivity of several alkyl halides is based on their structures and functions associated with them. The carbon-halide bond of alkyl halides has a low density of electrons compared to aryl halides.
MAINIDEA Compare and contrast alkyl halldes and aryl halides. Who are the experts. They are a subset of the halocarbons similar to haloalkenes and haloaromatics.
On the other hand aryl halides are organic compounds having halogen atoms bonded covalently to benzene rings or aromatic groups. So when four carbon it um the Seeker parent name should be. So first youre selecting the longest gene.
Name the type of organic compound each substance represents. Consider all the primary halides in this experiment and rank them in order of reactivity in each reagent. CHCl 3 is chloroform CX 4 is carbon tetrahalide.
The halogen is a good leaving group. Since the neutral bonding pattern for halogens is one bond and three lone pairs the carbon and halogen always share a single bond. Name the following simple alkyl halides using common nomenclature.
Aryl halides also show dipole-dipole interactions. Vinyl Halide Remember how to expand condensed formulas. Label each as primary secondary tertiary allylic or benzylic.
This problem has been solved. Draw the structures of all the alkyl halides that will be used in this experiment. And also if it is allylic or benzylic.
The carbon atoms here are in a cyclic orientation. Classify each halo compound shown below as an alkyl vinyl or aryl halide. The order of elimination reaction is.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. If the compound is an alkyl halide indicate whether it is 1 2 or 3. One alkyl halides or haloalkanes in which hydrogen atoms of alkanes are replaced with halogen atoms and the other aryl halides or haloarenes in which hydrogen atoms of arenes are replaced with halogen atoms.
Well also learn how they are formed why they are important and what further reactions can be done with an alkyl halide. Aryl halides These are the compounds in which the halogen atom is directly. Alkyl halide or haloalkanes are formed by the replacement of hydrogen atoms in an aliphatic hydrocarbon by halogen atoms Fluorine chlorine bromine or iodine.
These are named by naming the alkyl group attached to halogen and adding the name of the halide. Stones 50 percent-pearls for nails and 3D-jewellery permit you to switch an ordinary manicure into a get the job done of art. Only one C CH 3 X Primary Secondary and Tertiary Geminal and vicinal Nomenclature - All 16.
The general formula of aryl halides is ArX where Ar is phenyl substituted phenyl or aryl groups.

Solved Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Begin Array L Text A Chlorobenzene Text B 1 Text Bromo 4 Chlorohexane Text C 1 2 Text Difluoro 3 Iodocyclohexane

Solved 32 Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Chegg Com
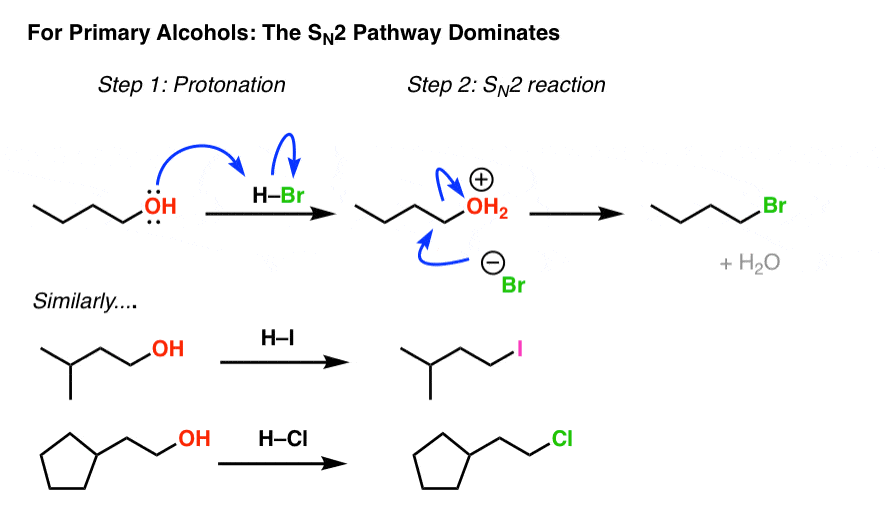
Making Alkyl Halides From Alcohols Master Organic Chemistry
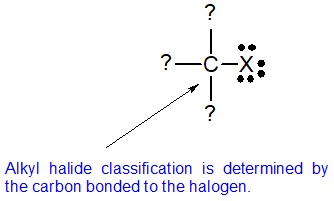
7 1 Alkyl Halides Structure And Physical Properties Chemistry Libretexts
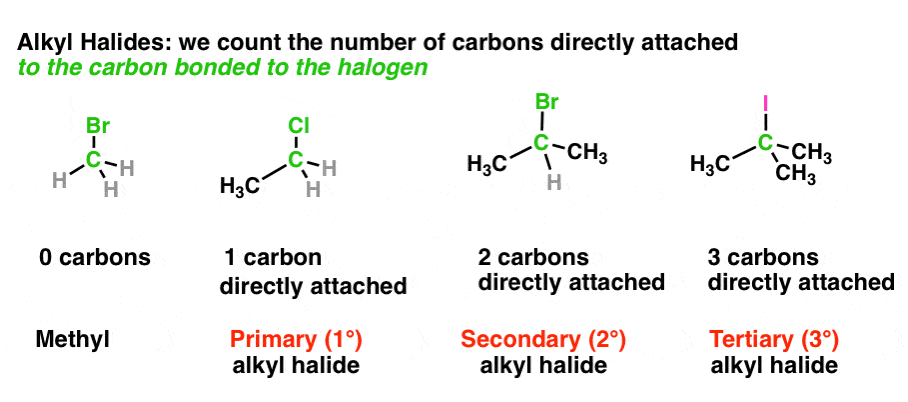
Primary Secondary Tertiary And Quaternary In Organic Chemistry
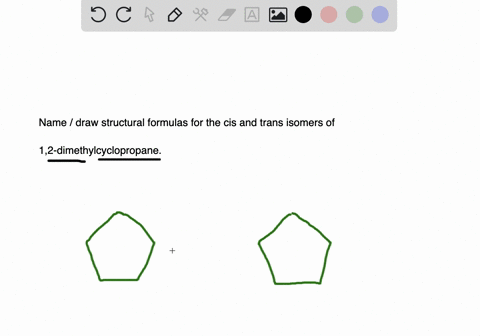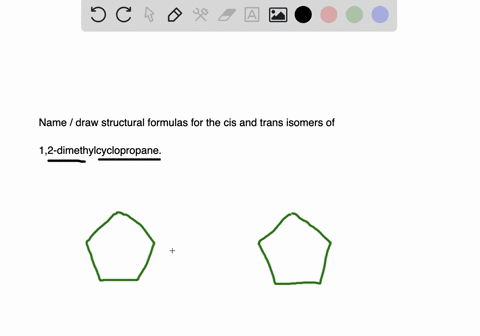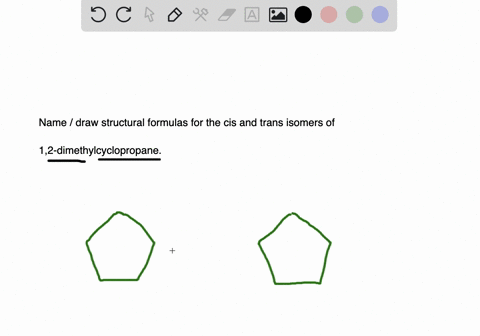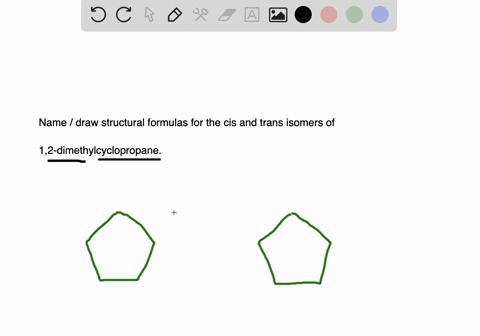
Solved Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Begin Array L Text A Chlorobenzene Text B 1 Text Bromo 4 Chlorohexane Text C 1 2 Text Difluoro 3 Iodocyclohexane
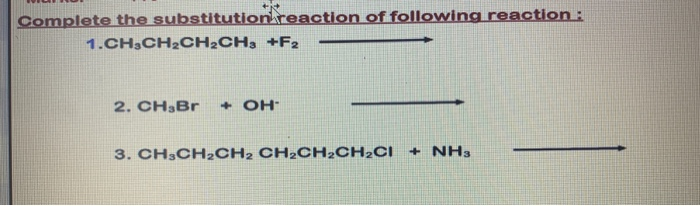
Solved 32 Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Chegg Com

Carbocation Rearrangements In Ring Expansion Reactions Practice Problem Reactions Chemistry The Expanse
0 comments
Post a Comment